Natural Language Processing (NLP) has transformed how search engines understand content, making it essential for savvy content marketers to adapt. If you’re feeling overwhelmed by technical jargon but know you can’t ignore this shift in SEO, you’re in the right place.
Most marketers still approach content creation with a focus on keywords, but… those days are almost over.
While your competitors stuff keywords hoping for better rankings, search engines have evolved to understand context, meaning, and user intent. Without adapting to these changes, you risk creating content that speaks to algorithms of the past rather than the sophisticated NLP systems of today.
During my years helping content teams navigate the complexities of SEO, I’ve seen firsthand how implementing NLP-friendly strategies can dramatically improve visibility and engagement.
The shift from keyword density to semantic relationships is a fundamental change in how we create content that resonates with both humans and search engines.
In this article, I’ll break down NLP in simple, practical terms specifically for content marketers. We’ll explore how today’s search engines actually understand your content, why topic clusters now outperform keyword targeting, and the actionable strategies you can implement without needing a technical background.
I’ll also cover the future of NLP in search and how to position your content strategy for success in 2026 and beyond.
Whether you’re responsible for a small blog or managing content for a large organization, understanding these principles will give you a significant advantage in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.
What is natural language processing (NLP)?
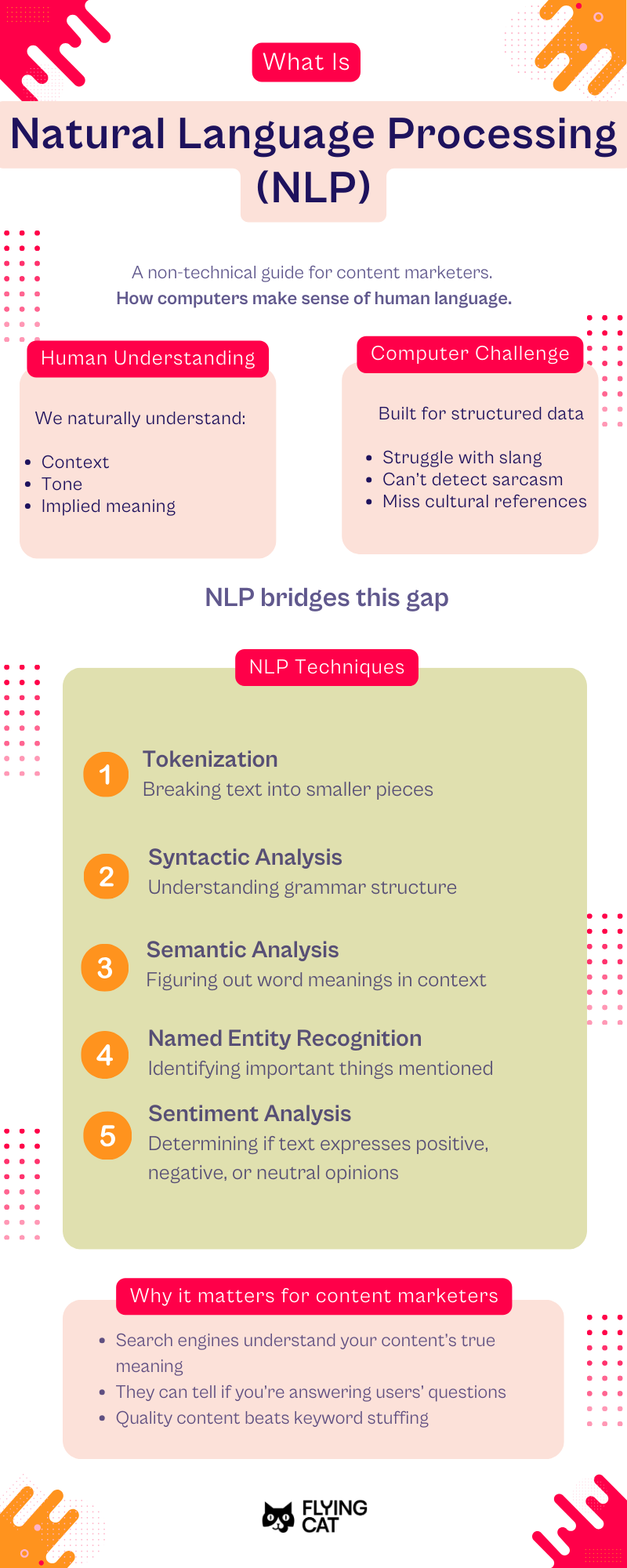
Natural language processing is how computers make sense of human language.
Think about how you naturally understand conversations. When your friend says, “This meeting is dragging on forever,” you know they’re bored, not that the meeting is literally infinite. You understand context, tone, and implied meaning without thinking about it.
Computers don’t have this natural ability. They’re built to process structured data like spreadsheets, not messy human language with its slang, sarcasm, and cultural references.
NLP bridges this gap using several techniques:
Tokenization: Breaking text into smaller pieces (like separating “Let’s eat, Grandma!” into individual words)
Syntactic analysis: Understanding the grammar of a sentence (recognizing “dog bites man” means something different than “man bites dog”)
Semantic analysis: Figuring out what words actually mean in context (knowing that “apple” in “apple pie recipe” means fruit, not a tech company)
Named entity recognition: Identifying important things mentioned in text (like people, places, organizations, and products)
Sentiment analysis: Determining if text expresses positive, negative, or neutral opinions
For content marketers, you don’t need to understand all the technical details. What’s important is that search engines now use NLP to understand:
- What your content is truly about (beyond just the keywords you use)
- Whether your content actually answers the questions users are asking
- How topics and ideas connect to each other
This means Google can now tell the difference between content that’s packed with keywords but lacks substance, and content that genuinely provides value to readers—even if it doesn’t use the exact search terms.
How NLP impacts search in 2025
Remember when SEO meant strategically placing keywords throughout your content? Those days feel increasingly distant. Google’s natural language processing has transformed how search engines understand content, making context and meaning far more important than keyword density.
The evolution from basic algorithms to sophisticated language understanding has been remarkable. BERT, introduced in 2019, was Google’s first major step toward truly understanding context in search queries. It could finally grasp the difference between “how to apply for Apple” (the company) versus “how to apply apple cider vinegar” (the product).
Today’s NLP models go much deeper. They comprehend relationships between topics, recognize entities without explicit mentions, and interpret user intent with impressive accuracy. This shift fundamentally changes how content marketers need to approach SEO.
When someone searches “project management solution communication issues remote teams,” Google doesn’t just match those keywords. It understands:
- The entity (project management software)
- The problem context (communication challenges)
- The specific environment (remote work)
- The implied intent (finding a solution to fix a problem)
This affects your content strategy in three critical ways:
- Traditional keyword research isn’t enough. You need to map entire topic ecosystems around your products and services. Tools like Neuron Writer or Surfer SEO can help identify NLP keywords that top-ranking pages are using for similar topics.
- Search is increasingly conversational. Voice searches and natural language queries have changed how people interact with search engines. Content that addresses questions in a natural, flowing manner performs better.
- Featured snippets have evolved. It’s now AI Overviews and soon-to-be AI Mode. Position-zero results allow users to get answers without clicking through to websites. Creating content that directly answers specific questions while providing additional context helps capture these opportunities.
Perhaps most significant is how AI chat interfaces are changing search behavior entirely. Users now engage with search through ongoing conversations rather than isolated queries, requiring content that anticipates follow-up questions and provides comprehensive coverage of topics.
For content marketers, the practical approach is to move beyond targeting individual keywords to creating interconnected content clusters. The most effective SEO strategies in 2025 treat content like a conversation, not a keyword-targeting exercise.
As Google’s understanding grows more sophisticated, focusing on truly helpful, comprehensive content that naturally incorporates relevant NLP terms will yield better results than manipulating keyword density or other outdated tactics.
NLP techniques for SEO optimization
Understanding how search engines process language is one thing. Applying that knowledge to optimize your content is another. Let’s break down the key NLP techniques that matter for your SEO strategy in 2025:
- Entity recognition
- Semantic search
Entity recognition: the backbone of modern SEO
Keyword stuffing stopped working with the Panda update in 2011. Now, the keyword will disappear as a whole.
Search engines identify and categorize entities (people, places, organizations, concepts) within your content. This shift from keywords to entities represents one of the most significant changes in modern SEO.
For example, when you mention “Salesforce” in your content, Google recognizes it as a company, a CRM platform, and part of the software industry. It understands these relationships without you explicitly stating them because its knowledge graph has mapped these connections.
Entities function as the technical backbone of topic clusters. While we’ve talked about topical authority for years in content marketing, entities provide the structure that makes these clusters meaningful to search engines.
To optimize for entity recognition:
- Use clear, specific terms for important concepts
- Include relevant entities your audience would associate with your topic
- Structure content to highlight relationships between entities
- Use schema markup to explicitly identify key entities
- Create content that thoroughly covers all aspects of an entity

Semantic search: connecting related concepts
Semantic search moves beyond literal word matching to understand the meaning and relationships between concepts. Google doesn’t just look for exact keyword matches. It looks for content that thoroughly covers a topic, including related terms and concepts.
That’s why the Skyscraper technique used to work – we’d make content longer, so it would more thoroughly cover a topic. We do need to cover it better rather than longer.
For instance, if you’re writing about “customer retention strategies,” Google expects to see related concepts like “churn rate,” “customer loyalty,” “feedback loops,” and “NPS scores.” The absence of these semantically related topics might signal that your content lacks depth.
To leverage semantic search effectively:
- Create comprehensive content that covers a topic thoroughly
- Include naturally related terms and concepts
- Build content clusters that interconnect related topics
- Focus on answering the questions your audience is likely to ask
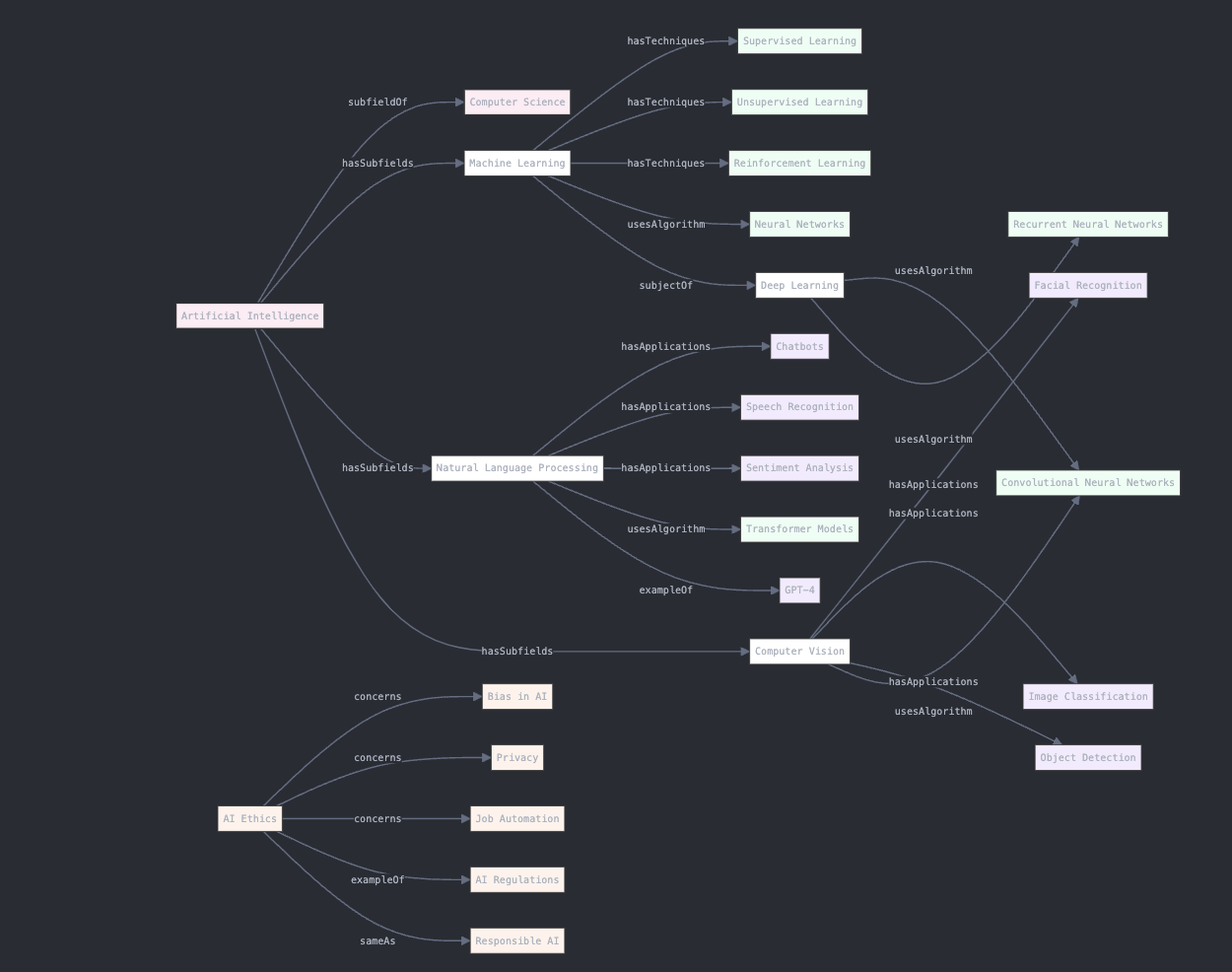
This knowledge graph shows how concepts connect through relationships:
- Nodes: The boxes represent concepts or entities (like “Artificial Intelligence” or “Machine Learning”)
- Edges: The lines with labels show relationships between concepts (like “subfieldOf” or “hasSubfields”)
- Hierarchies: The graph reveals parent-child relationships between topics
- Cross-connections: Some concepts connect to multiple areas (like how CNNs are used in both Deep Learning and Computer Vision)
This structure allows us to visualize how different concepts relate to each other in a network, rather than just a linear list or hierarchy.
Practical implementation: Tools and techniques
The most practical way to implement entity-based SEO is to use tools that help identify and optimize for entities. Here are some approaches that work:
1. Use NLP-powered content optimization tools
Tools like Clearscope (this is our preferred tool), Neuron Writer, Surfer SEO, and Frase analyze top-ranking content to identify entities and related concepts that should be included in your content. These help you find latent semantic index (LSI) secondary keywords. These tools can help you:
- Identify important entities and concepts related to your topic
- Determine the appropriate coverage depth for each entity
- Ensure you’re addressing the topic comprehensively
2. Implement entity-based schema markup
Schema markup provides explicit signals to search engines about the entities on your page. You can:
- Mark up your content with appropriate schema types (Organization, Person, Product, etc.)
- Define relationships between entities using structured data
- Provide additional context about entities through schema properties
3. Build entity-focused content hierarchies
Instead of organizing content solely around keywords, structure your site around entities:
- Create pillar pages that define major entities in your industry
- Develop supporting content that explores attributes and relationships of these entities
- Link content together in ways that reflect real-world entity relationships
4. Study Wikipedia’s content structure
Wikipedia provides an excellent model for entity-focused content:
- Start with clear definitions of the entity
- Include comprehensive attributes and characteristics
- Cover related entities and establish clear relationships
- Provide structured, organized information about the entity
Moving beyond basic NLP implementation
Advanced implementation of NLP techniques involves going beyond just including the right terms:
Topic classification and disambiguation
Search engines work to understand exactly which meaning of a term you’re using. For example, “python” could refer to a snake, a programming language, or the comedy group. Help search engines disambiguate by:
- Providing clear context in your introductory paragraphs
- Including related entities that clarify which meaning you’re using
- Using schema markup to specify entity types
What does this actually look like in practice, in-content and also looking at your topic selection?
If you’re writing about Python as a programming language, include related entities in-content like:
- Django (web framework)
- PyPI (package repository)
- Guido van Rossum (creator)
- Data science libraries like NumPy or Pandas
- References to syntax, coding, or development
Example 2: Python (snake) If you’re writing about pythons as snakes, include related entities like:
- Ball python, Burmese python (specific species)
- Reptile, constrictor (classification)
- References to habitat or behavior
- Snake handling or care
In practice, this might look like:
“Python is increasingly popular for machine learning applications, with libraries like TensorFlow and PyPI packages making complex data operations more accessible to developers.”
The presence of terms like “machine learning,” “libraries,” “TensorFlow,” and “developers” makes it crystal clear to search engines that you’re discussing the programming language, not the reptile.
Topic selection and content clustering
On a broader scale, this principle affects how you structure content across your site:
- Create context through content clusters: Develop related content pieces that reinforce the specific meaning of your target entity.
- Internal linking with descriptive anchor text: When linking to your Python programming tutorial, use anchor text like “Python programming basics” rather than just “Python.”
- Addressing multiple intents: For ambiguous topics, consider creating separate content pieces for each major meaning, then cross-link them with clarifications.
This approach helps search engines build a more accurate entity graph around your content, improving both ranking and visibility for the specific meaning you’re targeting.
Entity salience analysis
Google’s Natural Language API can show you which entities Google identifies in your content and how prominent (or “salient”) they are. This can help you:
- Confirm that Google recognizes the entities you’re targeting
- Adjust content to emphasize important entities more clearly
- Identify and fix cases where Google misinterprets your content
The most effective approach to NLP optimization isn’t trying to trick the algorithm. It’s creating genuinely helpful content that naturally includes the language, concepts, and relationships that both users and search engines recognize as relevant to the topic. When you thoroughly address your audience’s needs, you’re likely already incorporating the entities and relationships that NLP algorithms are designed to identify.
Related post: 6 Answer Engine Optimization Agencies Winning in AI Search
Actionable NLP SEO tips for content marketers
With NLP fundamentally changing how search engines interpret content, you need practical strategies that go beyond traditional keyword optimization. Here are actionable techniques specifically designed for today’s NLP-powered search landscape, including emerging considerations for generative engine optimization (GEO):
Think in topic clusters instead of single keywords
NLP has transformed how search engines understand content relationships, making comprehensive topic coverage essential:
- Build entity-focused pillar content that thoroughly defines and explains core concepts in your industry. For a marketing automation platform, create definitive guides on “customer journey automation,” “lead scoring systems,” and “behavioral email triggers” rather than targeting isolated terms.
- Map semantic relationships between your primary entities. When Google identifies your content’s entities, it also evaluates how well you demonstrate relationships between them. Show how lead scoring impacts email personalization or how behavioral triggers connect to customer journey stages.
- Implement intentional internal linking patterns that reflect real-world concept relationships. NLP models analyze your internal linking structure to understand how you connect ideas. Link related concepts in ways that reinforce their natural relationships, not just for link equity distribution.
- Conduct entity gap analysis against top-performing content. Use NLP tools to extract entities from top-ranking pages and identify concepts that competitors miss. Creating content that addresses these gaps provides unique value that both users and algorithms recognize.
- Address generative engine optimization (GEO) by structuring content to be properly interpreted by AI systems generating search responses. As search increasingly incorporates generative AI, organizing content with clear definitions and relationship statements helps ensure your content gets referenced in AI-generated answers.
Use schema markup to improve NLP understanding
Schema markup has become crucial for precise entity communication in an NLP context:
- Implement entity-defining schema that explicitly identifies the main entities on your page. For ambiguous topics, schema provides clarity that prevents misinterpretation by NLP systems.
- Create nested schema relationships that mirror the hierarchical structure of your content. Show how smaller concepts relate to broader topics using properly nested schema relationships.
- Include action-oriented schema properties like potentialAction to signal the functional purpose of your content. This is particularly important for generative engine optimization (GEO) as it helps AI systems understand what users can accomplish with your content.
- Add FAQ schema for entity disambiguation. FAQ schema lets you define related concepts clearly and answer common questions that might otherwise confuse NLP interpretation.
- Use specialized industry schema types relevant to your specific field. Schema.org offers hundreds of specialized types that can more precisely define industry-specific entities and relationships.
Write for humans first, but structure for AI models
The most successful content in 2025 satisfies both human readers and AI systems:
- Define entities explicitly before elaborating. Start sections with clear definitions of key concepts before providing details. This helps NLP models establish a baseline understanding of your topic.
- Use parallel structure for similar concepts. When discussing related ideas, maintain consistent formatting and structure. This pattern recognition helps NLP models identify and classify related information.
- Incorporate clear transition phrases that indicate relationship types between concepts. Phrases like “causes,” “results in,” or “is a component of” provide explicit relationship signals that NLP models can recognize.
- Build comprehensive entity profiles within your content. When introducing a key concept, ensure you cover its definition, attributes, relationships to other concepts, and practical applications. This complete coverage helps NLP systems build accurate entity representations.
- Focus on E-E-A-T signals specifically for generative engine optimization (GEO). As AI systems generate search responses, they prioritize content with clear expertise markers. Include credentials, experience statements, and attribution to help AI systems confidently reference your content in generated answers.
Leverage AI tools to optimize, not replace, content creation
AI provides powerful insights for NLP optimization without sacrificing human creativity:
- Use entity extraction analysis on draft content to verify NLP interpretation. Tools like Google’s Natural Language API show exactly which entities are recognized and how salient they are, allowing you to adjust content that’s being misinterpreted.
- Implement entity-based content briefs that specify required entities and relationships before writing begins. This ensures writers address all necessary concepts while maintaining creative freedom in execution.
- Apply context-aware semantic expansion to cover related concepts. Tools like Clearscope identify semantically related terms without requiring exact keyword matches, allowing for more natural writing that still satisfies NLP requirements.
- Test content with generative AI to evaluate generative engine optimization (GEO) potential. See how generative AI systems like ChatGPT interpret and summarize your content to identify areas where your key messages might be misunderstood or omitted in generated responses.
- Create entity-relationship visualizations to guide content planning. Mapping entity relationships visually helps ensure complete coverage of a topic ecosystem in ways that both human writers and NLP systems can understand.
The shift toward NLP and generative engine optimization requires rethinking content development at a fundamental level.
Rather than focusing on keyword placement, think about building comprehensive entity knowledge that clearly communicates relationships between concepts.
By implementing these strategies, you’ll create content that effectively communicates with both traditional search algorithms and emerging generative AI systems.
Future of NLP in SEO & what’s next
The technical architecture behind search engines is undergoing a fundamental shift that most marketers don’t fully grasp. Understanding this transformation at a deeper level reveals where SEO is headed and how to prepare:
Vector embeddings are replacing keyword indexes
The most profound change in search isn’t that it’s becoming conversational—it’s how search engines actually process and store content.
Traditional search relied on inverted indexes: essentially massive tables matching keywords to documents. When you searched, the engine would find matches and rank them using various factors.
Today’s NLP systems convert text into mathematical vectors—multi-dimensional coordinates that represent meaning, not just words. Google now sees your content as a collection of mathematical points in semantic space.
This explains why:
- Content can rank for terms it never mentions
- Exact keyword density has become irrelevant
- Conceptual relevance trumps keyword matching
For content creators, this means thinking about “semantic neighborhoods” rather than keywords. Your content exists in a mathematical space near similar concepts, and its position in this space determines when it appears in search results.
Cross-encoder models are redefining relevance matching
Search engines now use sophisticated neural networks called cross-encoders to determine relevance. These systems don’t simply match your content against a query—they process both simultaneously to determine conceptual alignment.
While traditional systems would count matching terms between query and document, cross-encoders identify semantic relationships that might not involve any shared terminology.
What this means practically:
- Content can rank for queries using completely different terminology
- The same word in different contexts triggers entirely different results
- Intent matching matters more than lexical matching
This explains why “traditional keyword research” is increasingly insufficient. Rankings depend on how well your content satisfies the intent behind a query, not how well you’ve optimized for specific terms.
Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) is reshaping how content gets used
The technical pipeline behind AI-generated answers is called retrieval augmented generation (RAG). Understanding this process reveals how content gets selected for inclusion in AI responses:
- The system retrieves relevant documents using vector similarity
- It evaluates which documents provide the most useful information
- It synthesizes an answer using information from these documents
- It attributes information to sources based on confidence and authority
This is increasingly how Google operates as well as LLMs like ChatGPT. Your content’s success depends on being selected during this retrieval phase and being deemed authoritative enough for inclusion in the generated response.
Success in this model requires:
- Clear entity definitions that match vector representations
- Comprehensive coverage that answers follow-up questions
- Structured content that makes information extraction straightforward
- Established E-E-A-T signals that increase confidence in your information
Topic modeling has replaced keyword targeting
Behind the scenes, search engines build complex topic models using techniques like Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) and more advanced neural approaches. These models identify clusters of concepts that tend to appear together.
Your content is evaluated against these topic models to determine its comprehensiveness and relevance. This is why “covering a topic thoroughly” has become more important than “using the right keywords.”
For example, when creating content about “customer retention strategies,” NLP systems expect to see related concepts like churn analysis, customer satisfaction measurement, loyalty programs, and feedback loops. Missing these expected connections signals incomplete coverage.
This topic modeling explains why:
- Pages that cover topics comprehensively outrank keyword-optimized pages
- Content clusters perform better than isolated articles
- Interlinked content that forms a coherent knowledge structure ranks better
NLP is merging context and queries into single representations
The most advanced NLP models now create unified representations of:
- The query itself
- The user’s search history
- Previous queries in a session
- Device context and location
- Temporal context (time of day, season, etc.)
This explains why identical queries can produce different results for different users or contexts. The query’s evaluation is merged with contextual information into a single mathematical representation, not evaluated in isolation.
For content creators, this means:
- Generic, one-size-fits-all content is becoming less effective
- Content that addresses specific scenarios performs better
- Understanding your audience’s context is as important as understanding their keywords
What these technical transformations mean for your content strategy
This deep understanding of NLP in search reveals several critical implications:
- Schema markup is becoming essential, not optional. Schema provides explicit entity definitions that help NLP systems accurately identify what your content is about and how it relates to other entities.
- Entity-relationship modeling should guide your content planning. Map the key entities in your domain and their relationships, then ensure your content accurately represents these relationships.
- Content atomization and recombination will become standard practice. Break content into well-structured, semantically clear components that can be retrieved and presented in different contexts.
- Predictable content structures help NLP systems interpret your information .Using consistent patterns for different content types helps extraction algorithms identify key information.
- Natural language generation (NLG) is affecting content evaluation. Search engines can now generate expected content for a topic and compare your content against this ideal representation.
The most successful content strategies will be those that align with how NLP systems build and maintain knowledge graphs. This means creating content that:
- Clearly defines entities and their attributes
- Explicitly states relationships between entities
- Provides comprehensive coverage of topics within your domain
- Organizes information in ways that facilitate extraction and synthesis
By understanding these technical foundations of NLP in search, you can develop content strategies that will continue to perform as search engines evolve from simple retrieval systems to sophisticated knowledge processors.

