If we can be certain about one thing, it’s that we never know for sure what the future holds. But if you’re investing in SEO, you may need to make a few predictions.
Forecasting SEO growth means you can show senior stakeholders what to expect in return for their digital marketing spend—not just keyword rankings and organic traffic, but also in terms of business growth. It’s a useful exercise that can help you make (and justify) strategic decisions for your business.
In this guide, we share our own tried and tested methods for forecasting SEO growth. We’ll talk you through these two models:
- Historical data forecasting: for businesses with existing web content and historical SEO data to guide them.
- TAM analysis: for businesses looking to use reoptimization of existing content to grow their SEO efforts—or even start from scratch.
We’ll also share our ROI calculator with you, so you can see how much revenue you can expect from your SEO spend.
Find out how much ROI you can expect from your SEO spend.
Get a copy of our SEO calculator to forecast good, better, and best scenarios for your search volume, conversions, and revenue.
Why forecast SEO growth?
SEO growth forecasting involves understanding and predicting:
- Keyword ranking positions in search engine results pages (SERPs)
- Organic search traffic
- Leads, conversions, and revenue
By combining this data, you’ll be able to assess the impact of SEO on your business.
It’s not an exact science. And Google has a habit of changing the rules just when you think you’ve got the hang of them. But there are some pretty big benefits to forecasting SEO growth:
- Know where to invest. For example, if you’re investing in B2B content writing services, forecasting SEO growth can help you predict how much this will increase your organic traffic growth.
- Get stakeholder buy-in. You can use forecasting figures to show current and potential investors your projected growth and revenue.
- Set KPIs and plan for the future. For example, knowing how many new team members to recruit and train.
- Make better data-focused decisions. For example, understand what you need to do to acquire new customers and get SQLs.
- Justify your SEO budget. When you can accurately forecast SEO growth, you can justify your budget to leaders and stakeholders.
SEO forecasting models and approaches
Let’s start by looking at some different ways to forecast SEO and how this can help you predict organic traffic, conversion rate, and revenue.
1. Forecasting from historical data
When you have at least a year’s worth of historical data from content that you’ve already published online, you can use it to understand how your site has performed in the past—and estimate what your potential traffic will be.
This approach uses mathematical formulas, like linear regression and exponential smoothing to make predictions on future organic traffic based on past trends.
Once you’ve forecasted organic traffic growth, you can add other metrics—like the number of paying customers and value per customer—to calculate how revenue will increase. We’ll look at this in more detail in our step-by-step guide below.
2. Forecasting using total addressable market (TAM) analysis
If you don’t have your own historical data, or want to know how a change in SEO strategy will impact your business, you can use a traffic estimation tool like Ahrefs to look at competitor sites to work out your total addressable market (TAM).
Your share of the TAM will depend on how big your budget is for investing in new content. But it’s worth knowing how many potential customers there are. You can then apply an expected penetration percentage for your own revenue forecasts.
Let’s say you’re launching a banner-creation tool and want to determine your TAM, you can look at Canva’s traffic figures on Ahrefs for the search term ‘banner’ to estimate the likely size of your market.
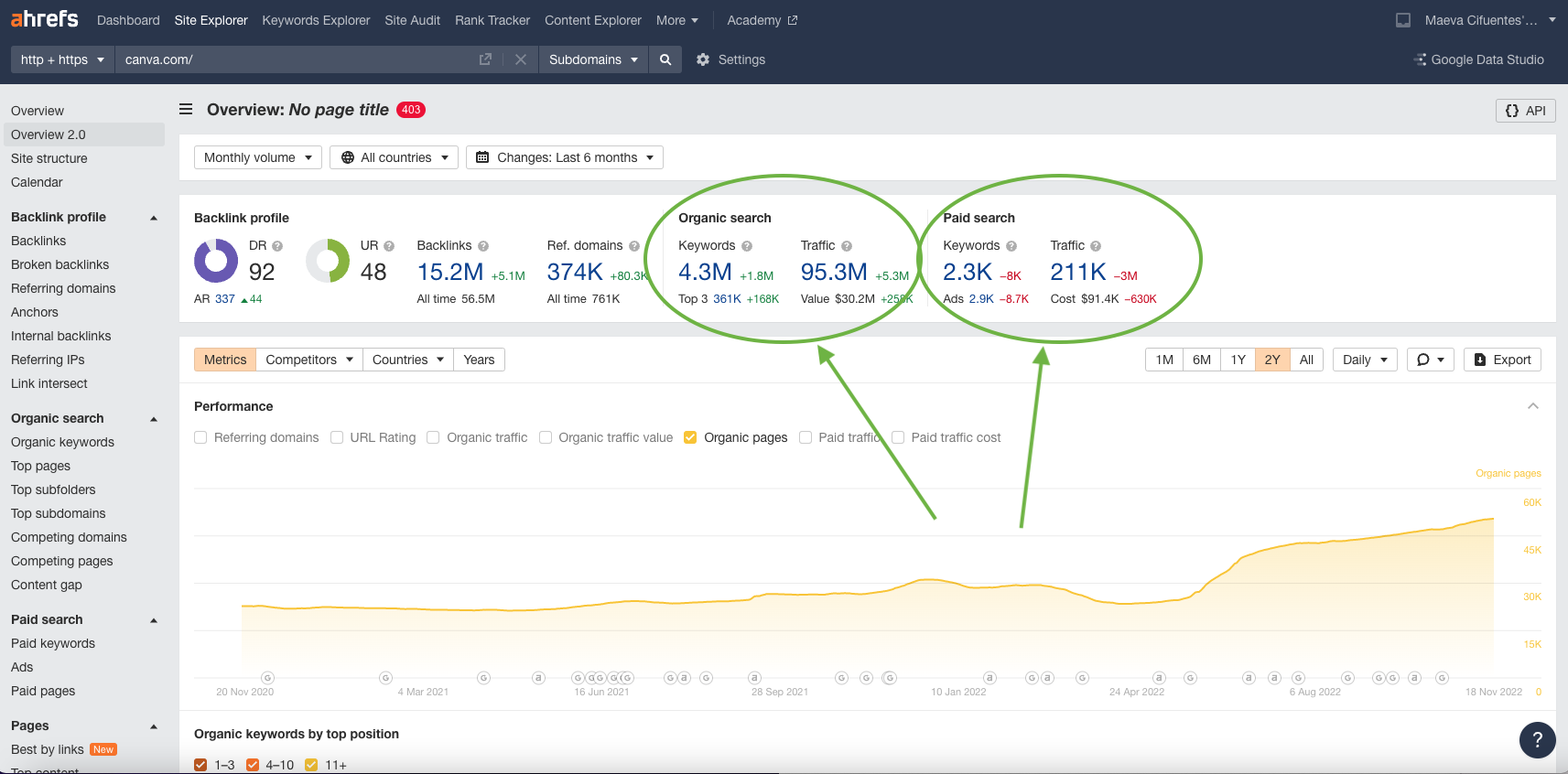

You can find out metrics like organic search and paid search for any website using a traffic estimation tool like Ahrefs.Source: Ahrefs
You can then use keyword forecasting to predict how much organic traffic certain keywords will bring you.
How to forecast SEO growth (step-by-step)
Let’s go through the steps for each forecasting model. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Google Analytics or Ahrefs to find out your monthly organic traffic (or your competitors’)
- Google Search Console for keyword positions and CTR
- Ahrefs for keyword research and search volume
- This growth forecasting template
- This historic performance forecasting template
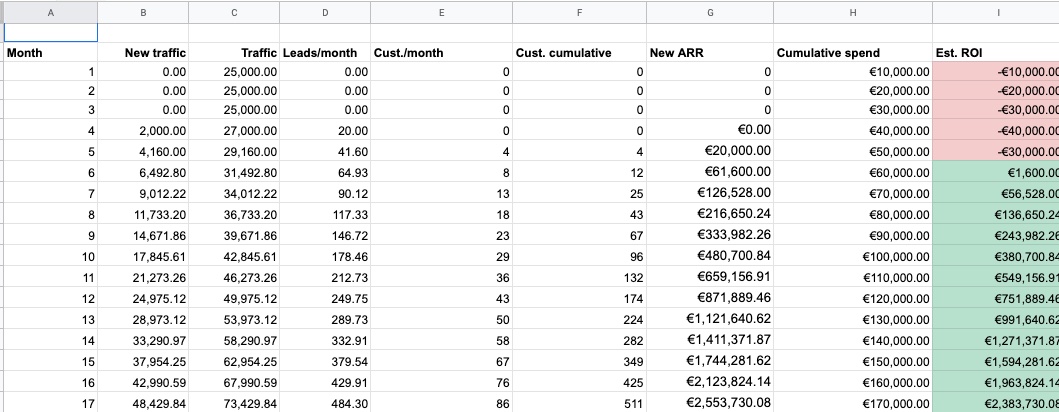

Forecasting SEO growth using historical data
If you’ve been producing content for a while and have one or two years of data, you can use it to forecast organic traffic for each month.
This method works best if you plan to continue along the same content production path and don’t intend to make any major changes to your SEO efforts.
Step 1. Pull your organic traffic data from Google Analytics
Go to Google Analytics > Audience. The data you need to collect first is your total organic traffic.
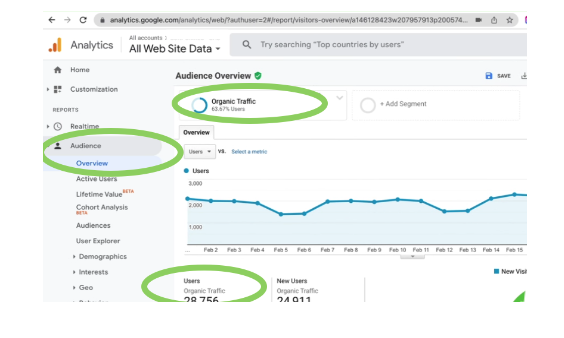

Source: Google Analytics
Step 2. Add your traffic figures to your historic performance template
Add your traffic data to column B of our historic performance template.
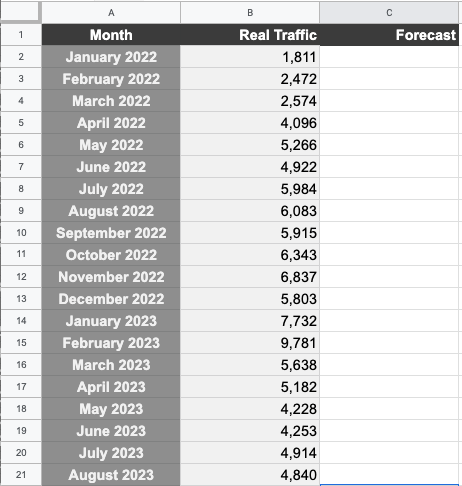

Then, collect the percentage growth by looking at the variation of growth month over month in terms of your users. You need to work out February monthly users minus January monthly users divided by January users. Here’s the formula:
{B3 (feb) – B2 (jan)} /B2
You’ll now be able to view your SEO forecast over the coming months and create a line graph to visualize your organic growth projections.
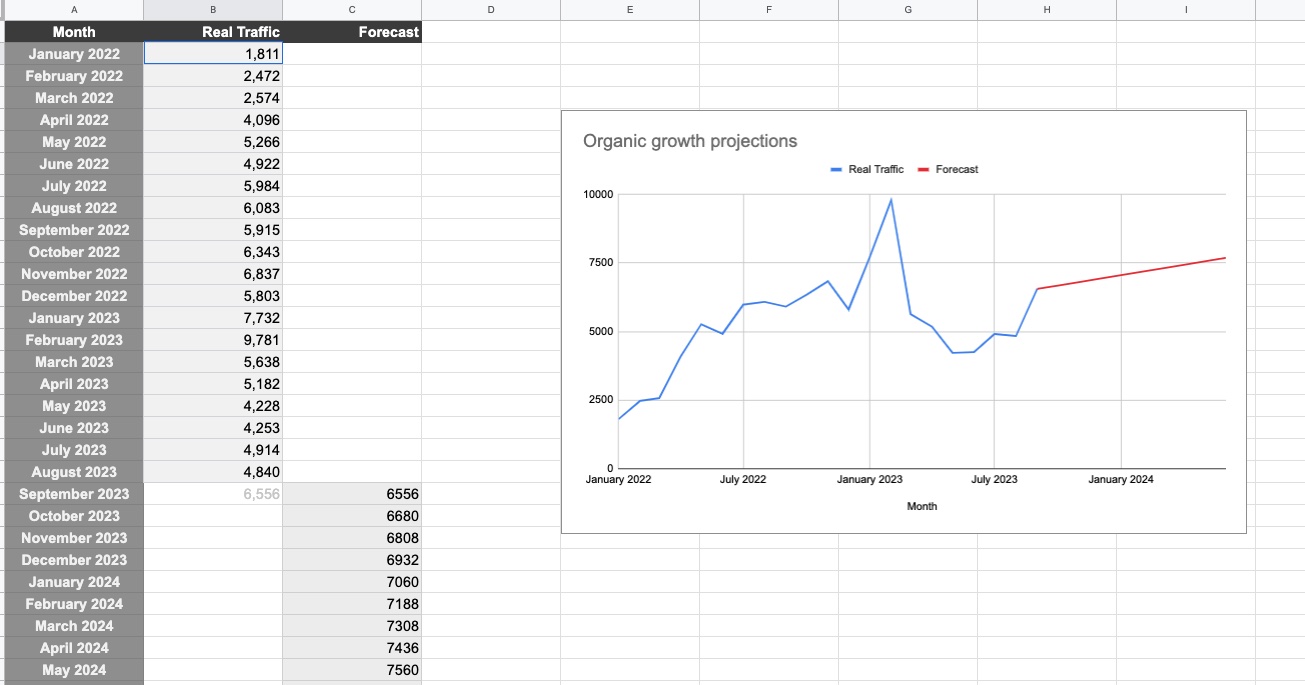

By looking at your historical data, you can calculate month-on-month growth and forecast future organic traffic.
Step 3. Look for trends and anomalies
To make your forecast as accurate as possible, you need to account for trends (e.g. seasonality) and take out any anomalies.
Look at your data to spot any seasonal trends, like a quiet period around the Christmas holidays or a spike in usage before summer. You can include these trends in your forecast for the next 12 months.
Anomalies are a rise or dip in traffic volume that can happen after a particular ad campaign or site redesign. Or when Google changes its algorithm, which can affect keyword ranking and how well your site’s pages perform in SERPs. These anomalies won’t be representative of future growth so you can take them out.
Forecasting SEO growth using TAM analysis
In the previous example, we looked at how you can forecast SEO growth if you don’t plan to change anything. If you want to increase your SEO efforts and content velocity—or don’t have any historical data—then TAM analysis is your best bet.
Using TAM analysis, you can look at your competitors to assess the opportunity that exists and estimate how much potential traffic you can expect to gain based on their data.
Step 1. Competitor analysis
Identify two or three market leaders in your industry. For example, if you’re launching a banner design tool, you can look at Canva for keyword inspiration and traffic data.
For each competitor, take their total traffic and divide this by their total number of pages to find out how many visitors each page is getting. You can find out your competitors’ traffic using Ahrefs.
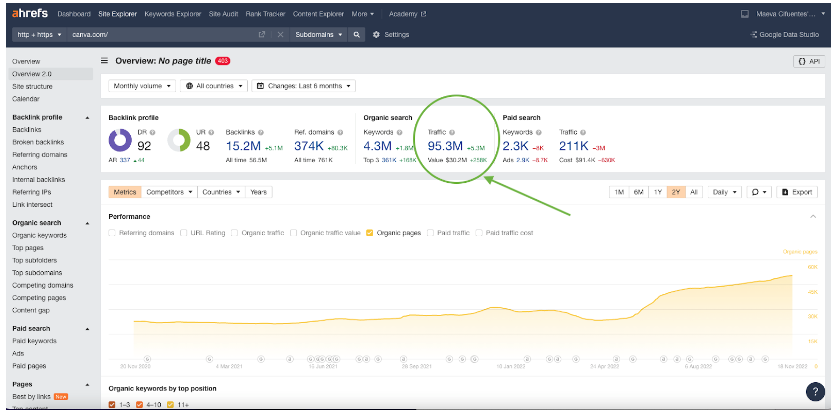

In this screenshot from Ahrefs, you can see Canva’s organic traffic.Source: Ahrefs
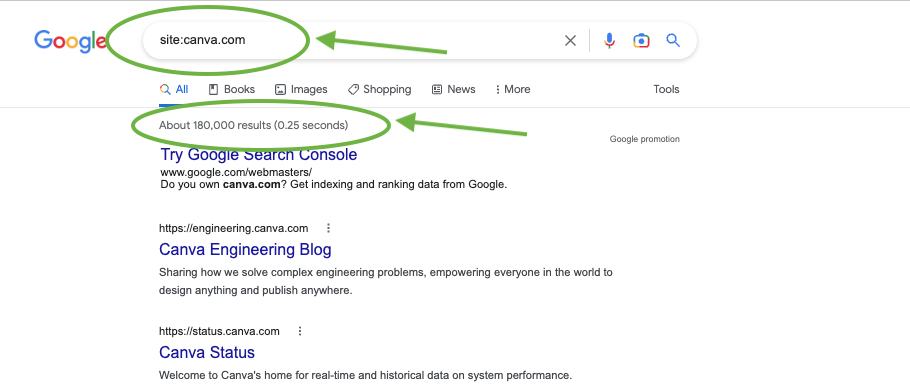
Then, you can find the number of pages a site has indexed on Google by searching site:domain.com.

Pro tip:
As well as telling you how much traffic your competitors are getting, and therefore the size of your TAM, you’ll discover how many pages you need to build if you want to aim for the same scale as your competitors.
How fast you can capture traffic data will depend on how fast you can create the content—and how much spend you can devote to content creation on a month-by-month basis. If you know you need to create 20 pages each month to match your competitor, you can start to work out the likely cost of your content-building strategy.
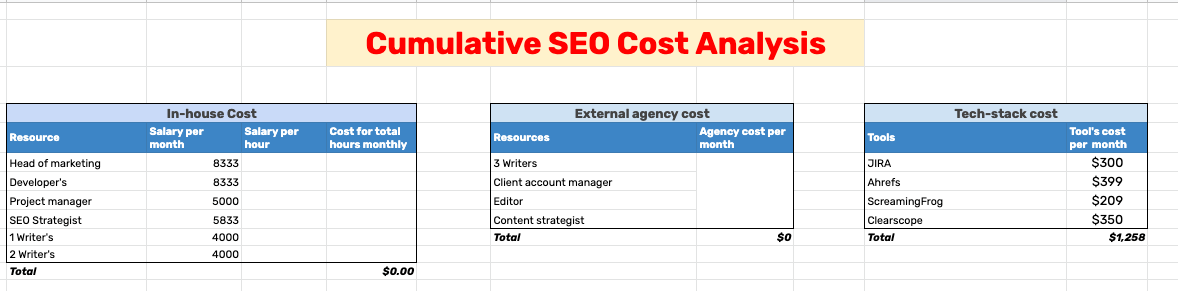

Calculate your spend on in-house and external SEO specialists, along with your tech-stack, to work out the monthly cost of your content strategy.
Step 2. Do your keyword research
Keyword forecasting involves using keyword search volume and average click-through rates (CTRs) to predict organic traffic.
To do this, you need to multiply two figures:
- Monthly search volume: the number of times per month that someone searches for a certain keyword (in a particular location)
- CTR: the average number of clicks that your page receives divided by the number of times your page appears in a search result.
You can find out the monthly search volume of keywords on Ahrefs. For example, you can look for the entire search volume for a keyword like ‘banner’ across all sites in the world or in a particular region.
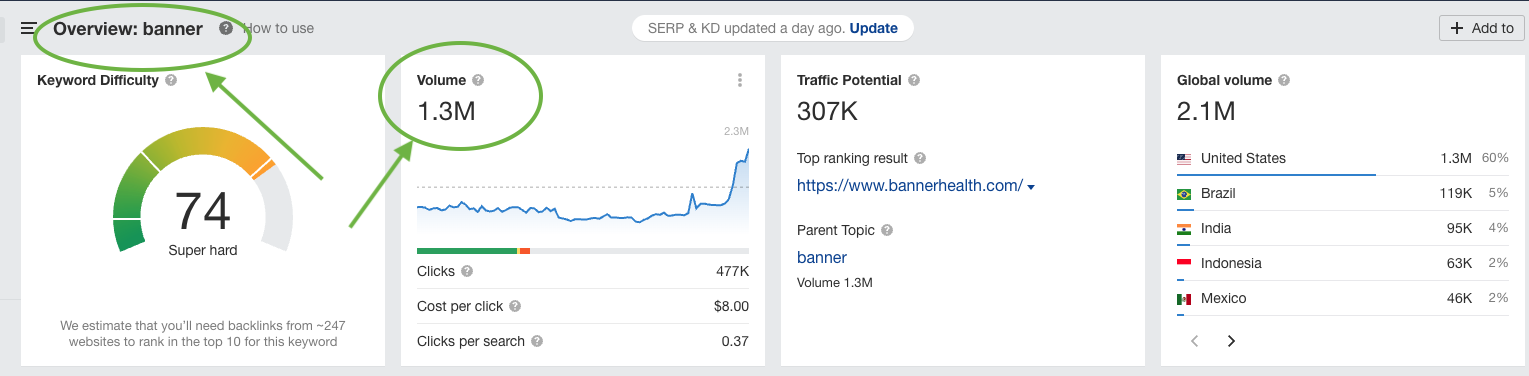

Source: Ahrefs
You can also see how a keyword performs on a particular website, like Canva.
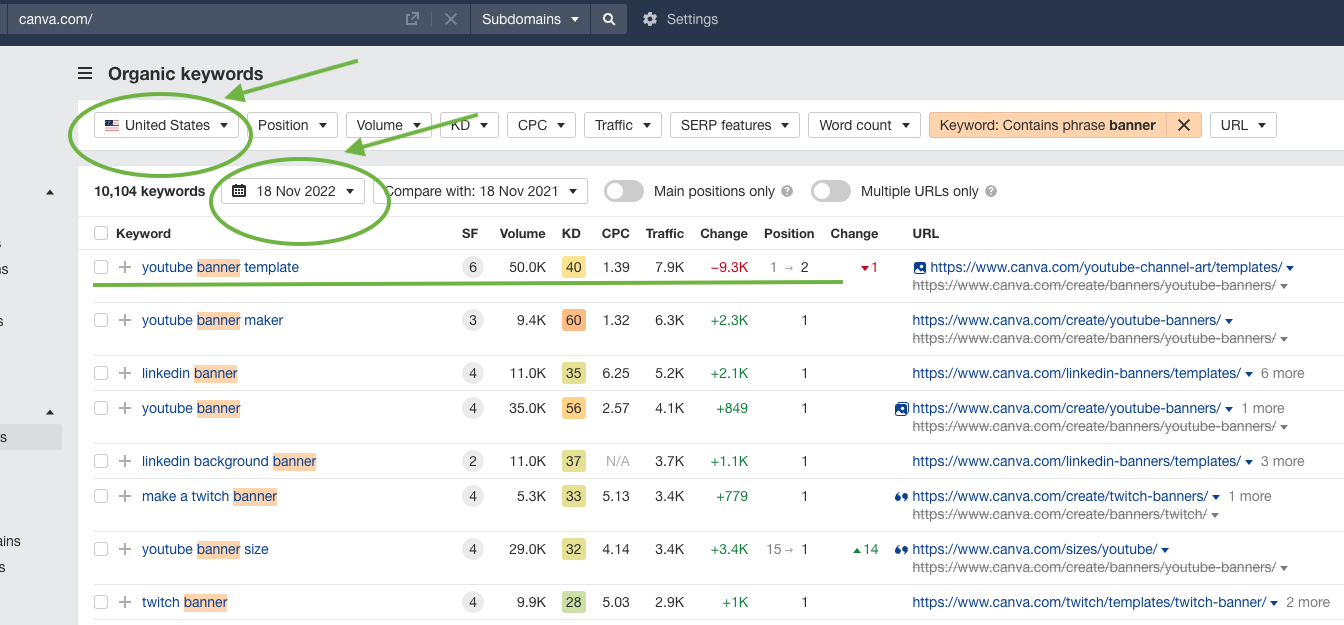

Ahrefs shows you interest in a keyword and lets you filter by region and time period.Source: Ahrefs
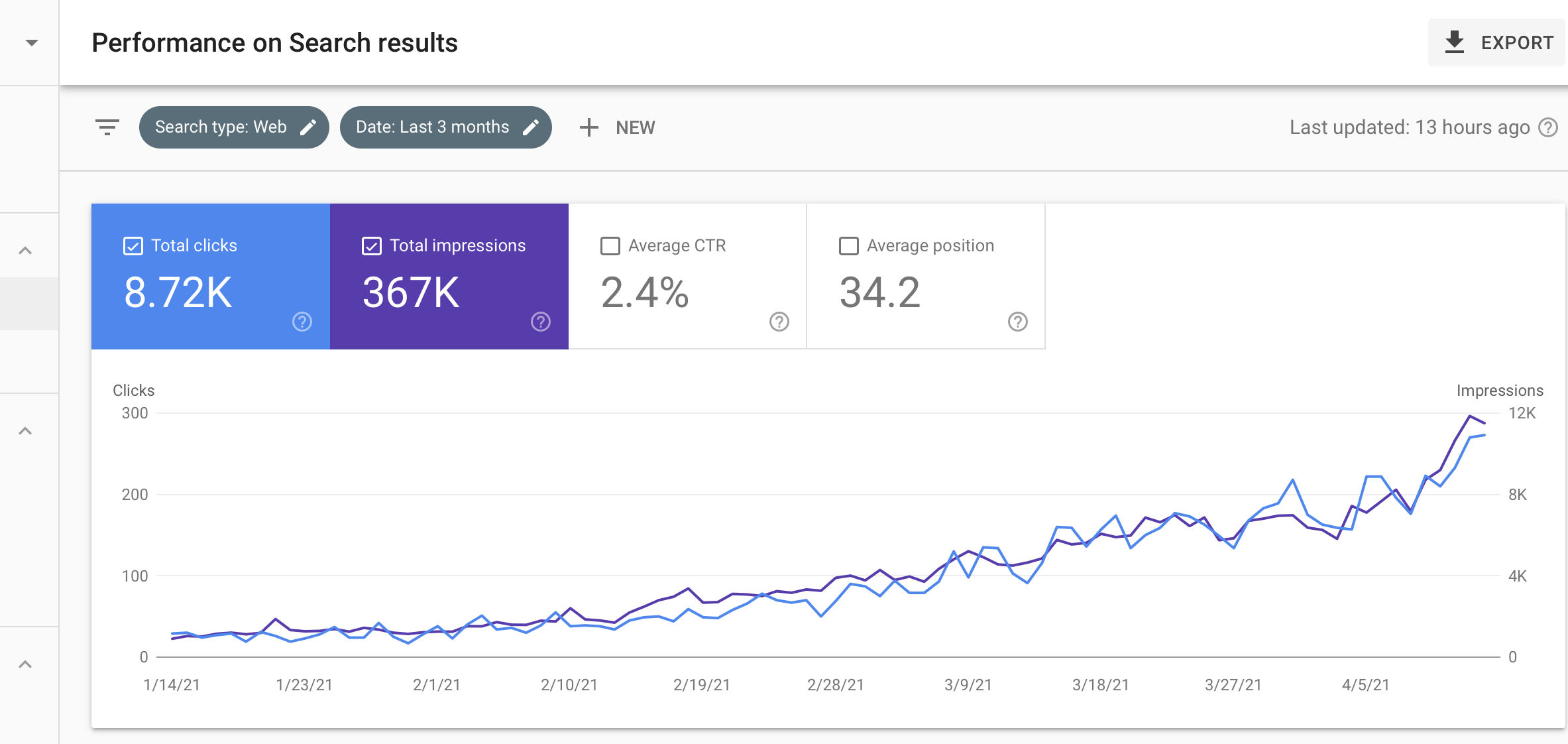
To find out your average CTR, use Google Search Console.
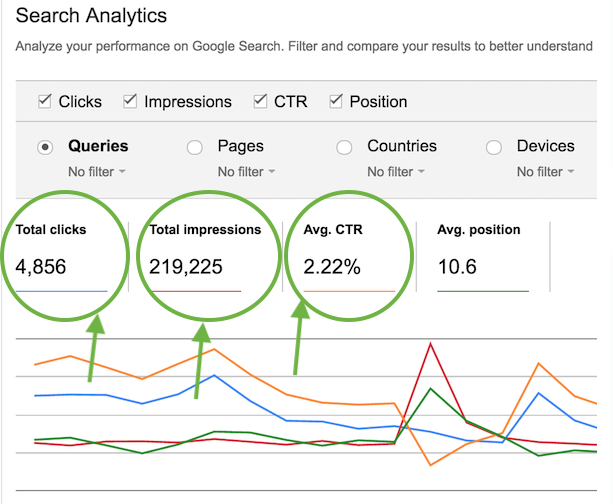

Source: Google Analytics
Now that you know your monthly search volume and clickthrough rate, you can calculate organic traffic.
For example: 100 (search volume) × 20% (CTR) = 20 monthly organic traffic
To find out how much potential traffic you can expect if you start ranking for target keywords, put them into a Google or Excel Sheet like this. It’s worth getting CTR data for all the ranking keywords (from 1 to 20).
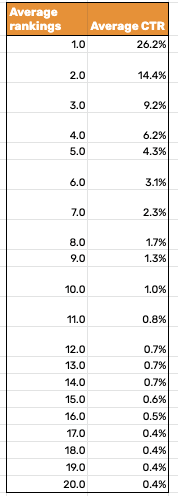

Step 3. Forecast paying customers
The remaining steps in our SEO forecasting process will work for either historical data or for projected traffic using TAM analysis.
Pro tip:
for a B2B SaaS tool, there are three key metrics that can help you understand your users and their journey to becoming paying customers:
1. Traffic to lead conversion rate: how often traffic leads to conversion, e.g. number of people arriving at a site and requesting a demo
2. Lead to paying customer conversion rate: the percentage of demo requests that convert to paying customers
3. Average customer value: calculated monthly, annually, or over lifetime
Now you know what your organic traffic should look like, you can start translating this data into paying customers and revenue.
1. Collect current customer figures from your Hubspot, Mixpanel, or any other analytics tool. If you don’t have current customer data, you’ll need to estimate this.
2. Add the customer figures to a Google or Excel Sheet like the one below. To estimate your total paying customers in February (assuming that’s your next month):
Take the estimated total traffic for February. Multiply it by the number of paying customers from last month and divide it by the total traffic.
For example 3000 x 200/3500 = 171 paying customers
→ Now you have an estimate of how many paid customers you’ll be getting.
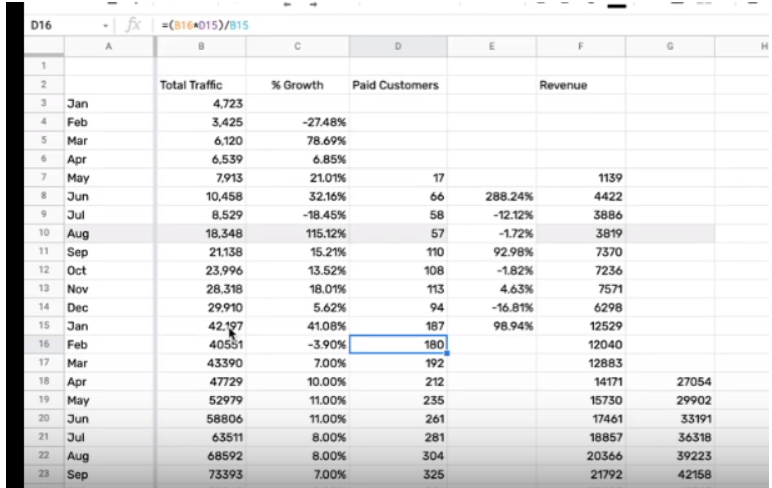

Step 4. Forecast revenue
Now you know how much traffic and how many paying customers you’re likely to get, you can add the value of each paying customer to help you forecast revenue.
To calculate your monthly revenue, multiply your average MRR by your estimated monthly paying customers.
For example MRR ($100) x paying customers (500) = monthly revenue ($50,000).
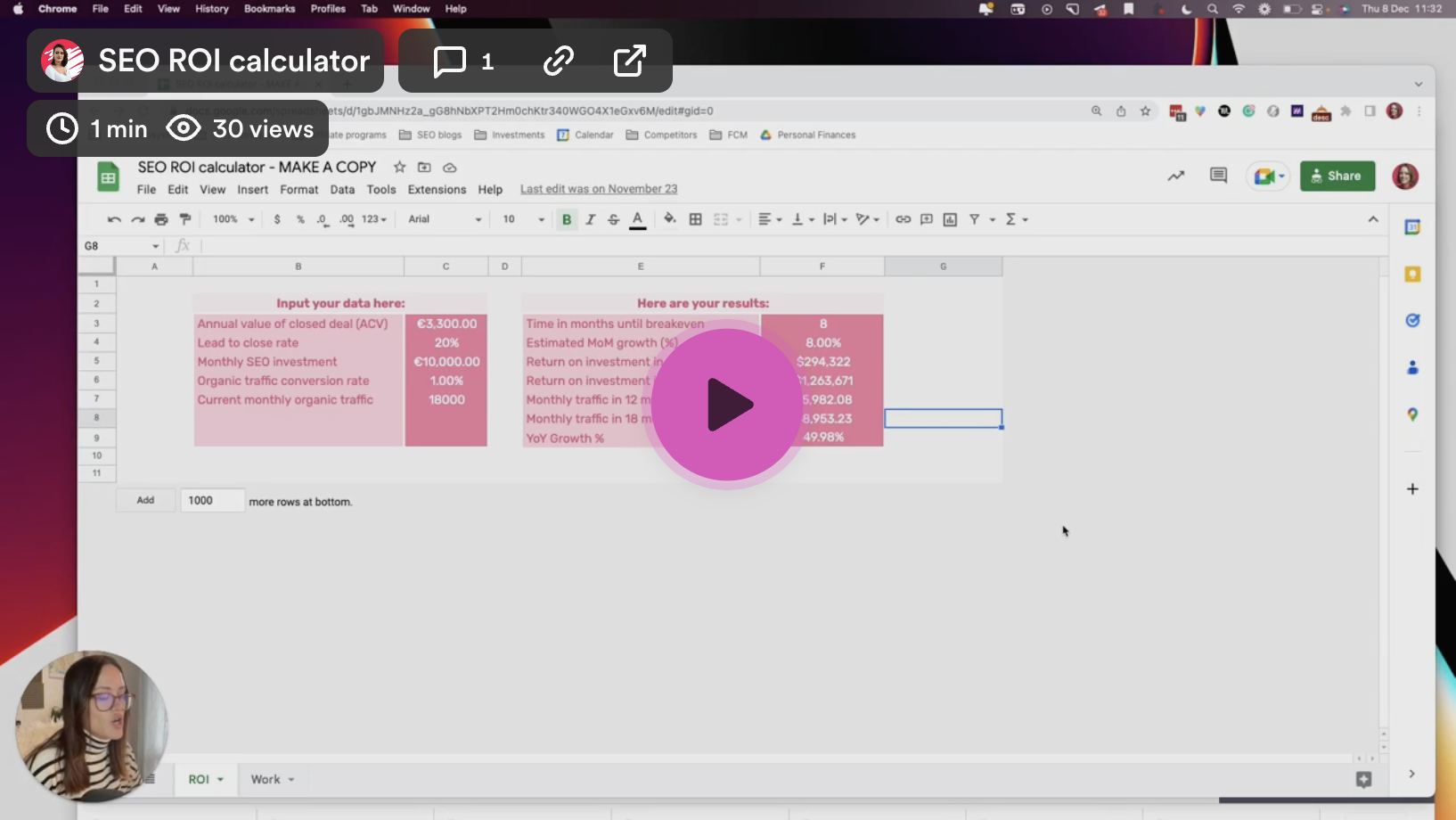
Try this SEO ROI calculator
Input your monthly data into the cells to forecast organic traffic and find out how much ROI you can expect from your SEO spend. You can use the SEO calculator to calculate the time it will take to break even and see your month-on-month and year-on-year growth.
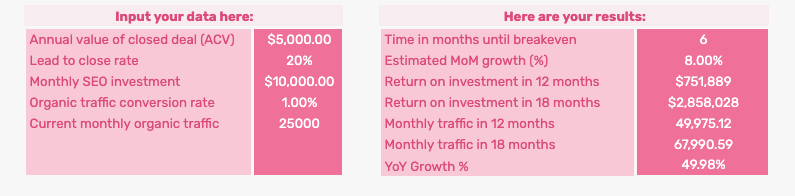

Find out how much ROI you can expect from your SEO spend.
Get a copy of our SEO calculator to forecast good, better, and best scenarios for your search volume, conversions, and revenue.



Who needs SEO growth forecasting?
SEO forecasting is essential for every online business whether their main focus is B2B SaaS, enterprise software, or ecommerce.
Who should do it?
A dedicated SEO specialist or external SEO company is best placed to forecast SEO growth. But not everyone has the budget for a full-time SEO team. So, the ultimate responsibility for planning SEO budget and strategy often falls to the marketing department.
When you take a holistic approach to SEO and view it as a key driver for business growth, all the stakeholders across your company from sales to HR should be involved. If you decide you want to dedicate a significant budget to SEO or want to hire a B2B SaaS SEO agency, then you’ll need to invest not just in SEO but in sales and customer service teams as your business grows.
When to avoid it
If you don’t know why you’re doing SEO, and just feel it’s another item to check off your marketing to-do list, you should probably give it a miss.
Randomly picking keywords you want to rank for and chucking money at content you think might attract customers without careful planning is unlikely to give you a good (if any) return on investment.
Forecasting SEO growth to understand the future of your business
When you forecast SEO, you’re not just predicting potential keyword rankings and search volume—you’re getting a glimpse into your company’s future business growth and revenue.
Whether you have an existing website with historical data or want to turn over a new page in your SEO strategy, you can use tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, Google Search Console, and Google Analytics to predict organic traffic growth to your website. And when you add customer numbers and values to your SEO data, you can see the real impact of your SEO strategy.
Want an accurate forecast for SEO growth?
We’ll design and implement a tailor-made SEO strategy for your business and tell you exactly what to expect from your SEO spend.

Frequently asked questions about forecasting SEO growth
What is the equation for forecasting SEO growth?
The equation for forecasting search engine optimization growth based on keyword search volume is: monthly search volume X CTR = monthly organic traffic
How is organic traffic growth measured?
Organic traffic growth is measured by subtracting the number of sessions last month (or year) from the number of sessions this month (or year). Divide the result by the number of sessions last month (or year) and multiply that figure by 100 to get a percentage.
What is web traffic forecasting?
Web traffic forecasting is a prediction of how many visits or sessions your website will get. You can forecast web traffic using forecasting models that take historical data from tools like Google Analytics and predict traffic changes based on factors related to your SEO spend.
What are the possible causes of SEO growth?
Some possible causes of SEO growth are
- Improved keyword rankings
- Increased search volume
- Organic traffic growth
- Improved quality content that offers value to your intended users
- Optimized pages that improve your site’s ranking
- Social signals, when people share your content on social media, and a positive user experience
Does SEO increase traffic?
SEO increases traffic to your website by making it more visible to users from search engines like Google. SEO will help your website rank as highly as possible, ideally on page one of search results.
