Search is changing. Users are turning to ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews for direct answers, bypassing traditional rankings. If AI tools aren’t surfacing your content, you’re invisible where it matters most.
That’s where generative engine optimization (GEO) comes in. GEO ensures AI-driven platforms don’t just recognize your content but actively cite and retrieve it in their responses.
This guide breaks down why AI-driven search is reshaping SEO and how to optimize for AI visibility. If you want your content to stay relevant in a world where search engines generate answers, here’s what you need to know.
What is generative engine optimization?
Just as search engine optimization (SEO) focuses on making your content visible in Google’s search results, generative engine optimization (GEO) ensures your content appears in AI platforms’ responses. I hear more and more people telling me they’re using ChatGPT or Perplexity now for different use cases, instead of Google. While Google is still dominating search – you can’t ignore how the ecosystem is changing.
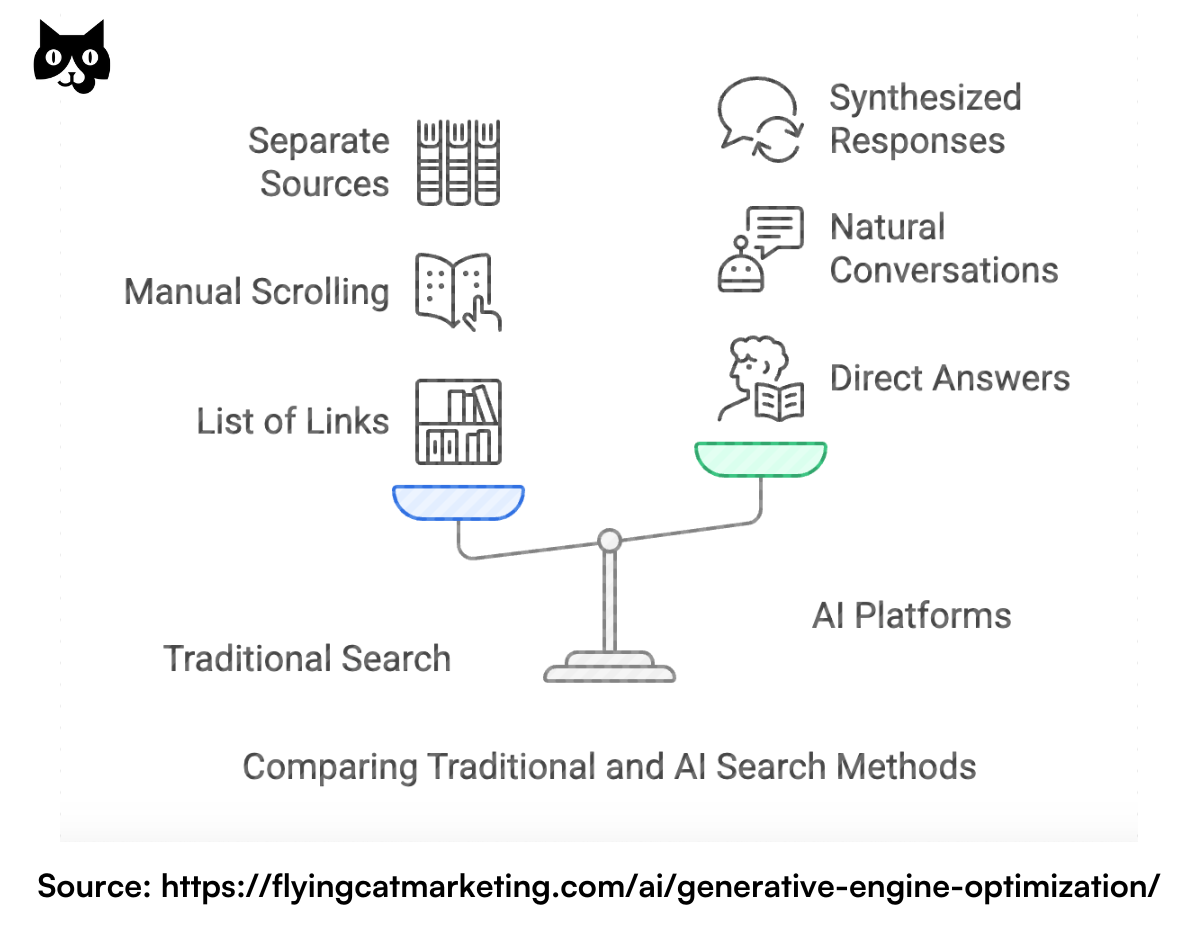
Think of traditional search like looking through a library catalog – you search for keywords, and Google shows you a list of books (websites) that might have what you need. GEO, on the other hand, is like having a knowledgeable librarian who not only finds the relevant books but reads them and summarizes the key information for you.
Understanding the shift in search behavior The numbers tell a compelling story. ChatGPT alone has over 300 million active weekly users and receives approximately 1.5 billion visits each month. For comparison, that’s nearly half the traffic of Netflix. Even more striking, Gartner predicts that by 2026, traditional search engine use will drop by 25% as people increasingly turn to AI platforms for answers.
Why? Because these platforms offer a fundamentally different way to discover information:
- Instead of scrolling through multiple websites, users get direct answers
- They can ask follow-up questions naturally, as if talking to a human
- The information is synthesized from multiple sources into one coherent response
How AI is changing content discovery
Traditional search engines rank content based on factors like keywords, backlinks, and user behavior. AI platforms work differently – they process and understand content more like a human would. When someone asks a question, these platforms:
- Understand the context and intent behind the question
- Pull relevant information from their knowledge base
- Create a new, original response that directly answers the question
For content creators and marketers, this means that when optimizing content, you ensure it’s understood and referenced by AI systems in a way that makes it more likely to be included in their responses.
Understanding how AI platforms get their information
To effectively optimize your content for AI platforms, you first need to understand how they find and use information. Think of these platforms as different types of research assistants – each with their own way of gathering and sharing knowledge.
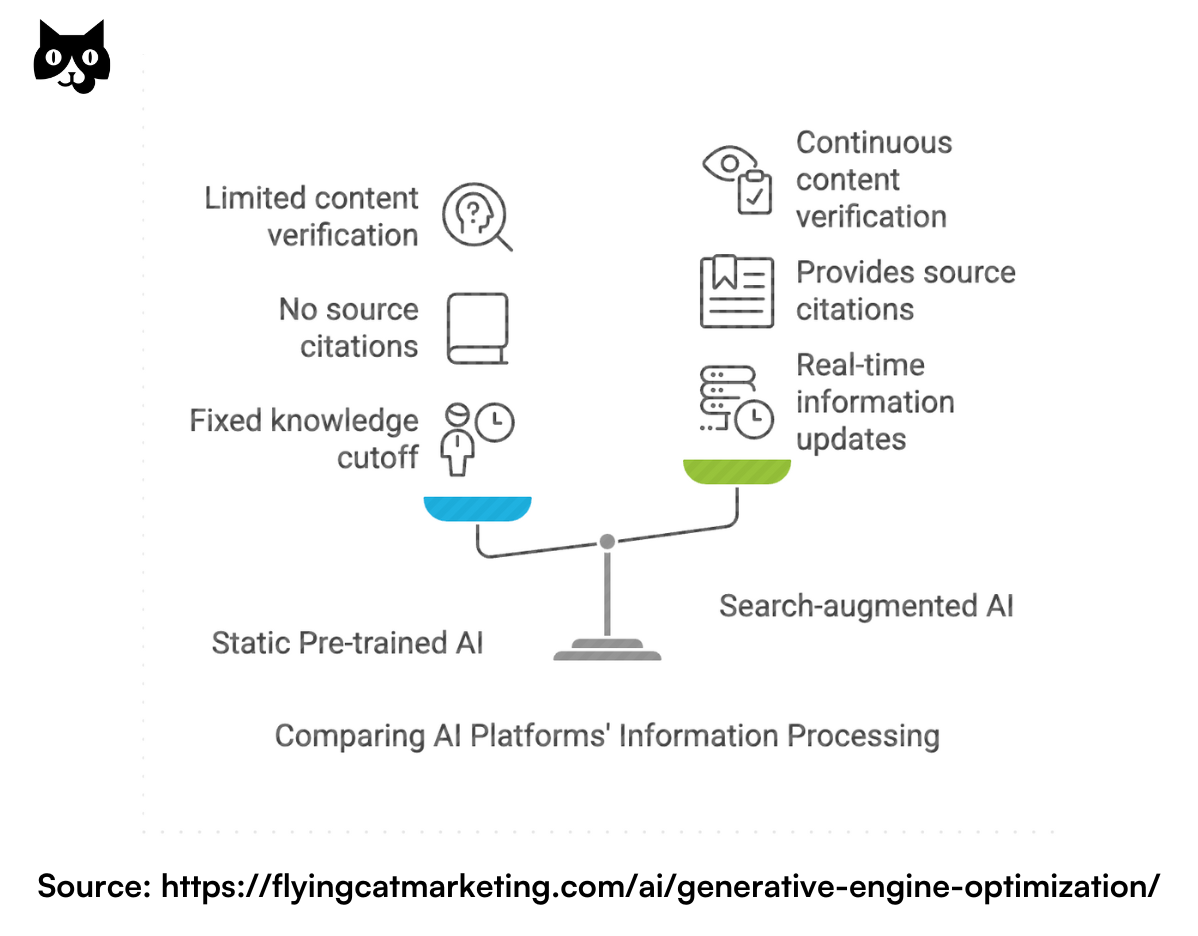
Static pre-trained AI platforms
The first type, which includes platforms like Claude and the free version of ChatGPT, works like a brilliant research assistant who has read and memorized an enormous library but is locked in a room without internet access. These platforms:
Key characteristics:
- Have a fixed knowledge cutoff date (Claude: April 2024, ChatGPT free: March 2023)
- Can’t independently verify or update their information
- Don’t usually provide links to sources
- Rely entirely on what they learned during their initial training
Real-world implications:
- If your content was published after their cutoff date, they won’t know about it
- They might reference your brand or content without attribution
- Their knowledge of your industry might be outdated
- They’re more likely to speak about established brands than new ones
For example: If you launched a revolutionary new product in January 2024, Claude (with an April 2024 cutoff) might know about it, but ChatGPT’s free version (March 2023 cutoff) won’t mention it unless specifically prompted with that information.
Search-augmented AI platforms
The second type, including Perplexity and certain models of ChatGPT Plus, is like a research assistant with both a photographic memory AND real-time internet access. According to our sources, these platforms receive about 400 million combined monthly visits.
Key characteristics:
- Combine their base knowledge with current information from the internet
- Provide direct links to sources
- Update their knowledge continuously through web crawling
- Can verify and fact-check information in real time
Real-world implications:
- Your content can be discovered as soon as it’s published and indexed
- You can receive direct referral traffic from these platforms
- They can cite specific pages and quotes from your website
- They’re more likely to provide current, verifiable information
For example: When someone asks Perplexity about current industry trends, it might directly quote and link to your latest blog post, driving traffic to your site.
How different platforms process your content
- Perplexity AI Crawling method:
- Uses its own crawler (PerplexityBot)
- Actively indexes new content
- Prioritizes authoritative sources
- Maintains its own web index
Perplexity Content processing:
- Combines multiple sources for comprehensive answers
- Provides direct citations with clickable links
- Shows source credibility ratings
- Updates information in near real-time
Real-world example: If someone asks about “best marketing automation tools 2024,” Perplexity might combine information from your product page, recent reviews, and industry reports, complete with direct links to each source.
- ChatGPT (Paid version) Crawling method:
- Leverages Bing’s search index
- Uses Microsoft’s web crawler
- Can access current web pages through Browsing feature
- Maintains conversation context while adding new information
- Was found to have crawled and transcribed millions of hours of YouTube videos
ChatGPT content processing:
- Verifies information through multiple sources
- Can navigate and understand complex websites
- Maintains user context through conversations
- Can process and analyze current web content
Real-world example: A user might start by asking about your product, and ChatGPT Plus can then browse your website in real-time to provide updated pricing, features, and customer testimonials.
Content optimization implications
- For static platforms:
- Focus on establishing strong brand presence in pre-2024 content
- Create comprehensive, evergreen content that’s likely to be included in training data
- Build strong industry authority through widely-referenced content
- Use clear, consistent brand messaging that’s easy for AI to understand and reference
- For Search-Augmented Platforms:
- Maintain strong technical SEO for crawler accessibility
- Keep content fresh and updated regularly
- Include clear citations and references
- Structure content with clear headings and sections
- Provide context and background information
- Use schema markup to help AI understand your content better
How traditional search engines and AI platforms complement each other
The relationship between traditional search and AI platforms reveals a fascinating shift in how people discover information. Rather than replacing search engines, AI platforms have created a new type of information-seeking behavior that’s more conversational, iterative, and complex.
Think of it like the difference between asking a librarian for help versus browsing library shelves yourself. Sometimes you want an expert to synthesize information and guide you, while other times you prefer to explore and draw your own conclusions. Both have their place, and increasingly, people are using both in harmony.
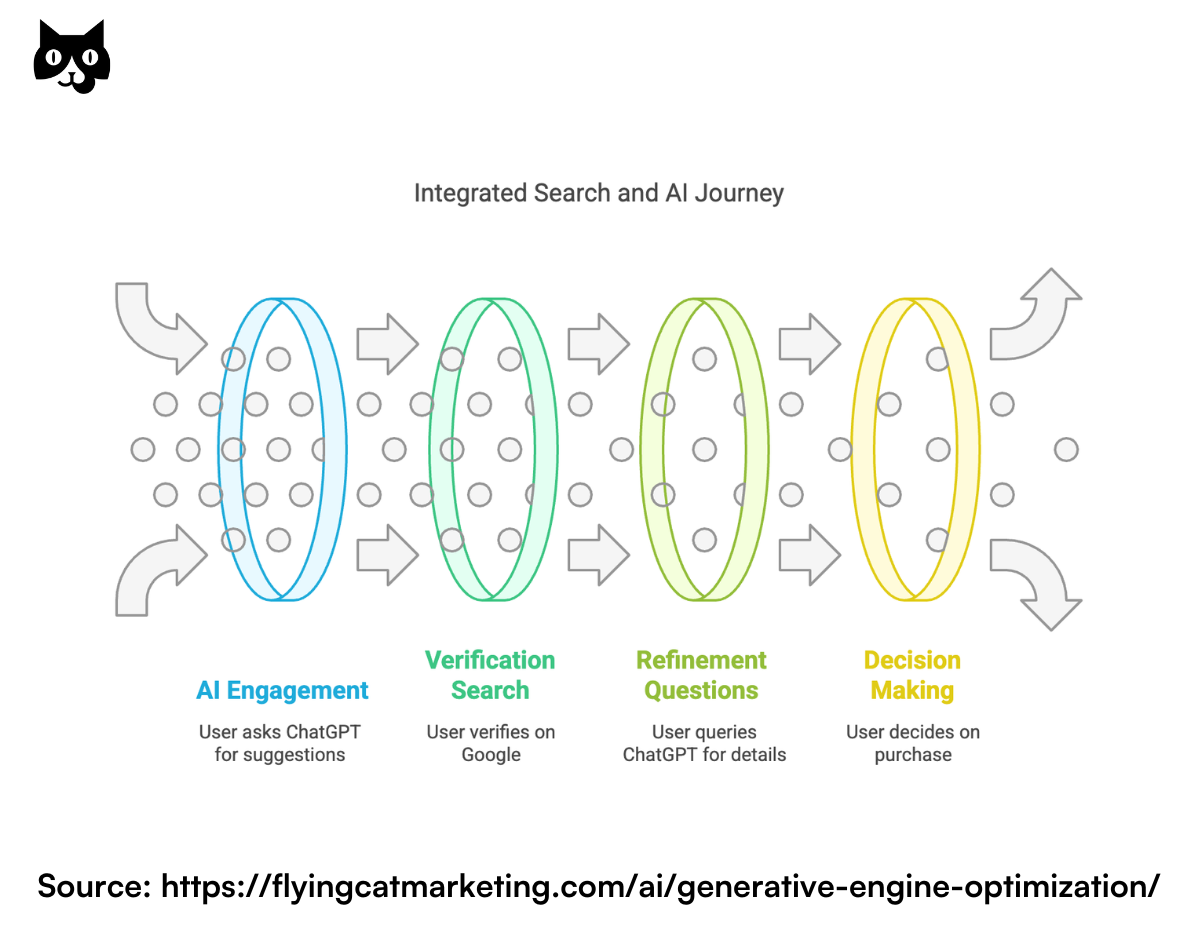
The real-world search journey looks something like this:
Scenario 1: Product research
- User asks ChatGPT for initial product recommendations
- Goes to Google to verify prices and read reviews
- Returns to ChatGPT to ask specific questions about features
- Makes final purchase decision after visiting brand website through Google
What’s fascinating about this behavior is how it represents a fundamental change in trust and verification. Users are leveraging AI platforms for their synthesis capabilities while relying on traditional search for verification and deeper research. This dual-platform approach is becoming the new normal, especially for complex purchasing decisions.
The evolution of search behavior presents both challenges and opportunities. Traditional search engines continue to dominate because they excel at:
- Visual content (images, videos, product photos)
- Recent news and time-sensitive information
- Local business information
- Price comparisons and shopping
- Direct access to specific websites
Meanwhile, AI platforms have carved out their own niche, particularly excelling at tasks that require deeper understanding and synthesis. They’re becoming the go-to choice for:
- Complex questions requiring synthesis of multiple sources
- Step-by-step instructions and explanations
- Personalized recommendations
- Technical troubleshooting
- Content summarization and analysis
The implications of this shift are profound. Consider what happened when one of our clients, a B2B software company, noticed an interesting pattern in their analytics. Their support documentation was simultaneously ranking well in Google and being frequently cited by AI platforms.
The traffic wasn’t being cannibalized – instead, they were seeing increased engagement from both sources. Users would find their content through an AI platform, verify it through Google, and then return through direct traffic for future needs. This created a virtuous cycle of visibility and authority.
This brings us to Google’s response: AI Overviews. More than just another SERP feature, this was Google’s step away from 10 blue links and toward synthesizing information sources. When Google launched AI Overviews globally, many SEOs feared it would decrease clicks to websites. However, what we’re actually seeing is more nuanced:
- They appear in prime SERP real estate, above traditional results
- Unlike featured snippets, they synthesize information from multiple sources
- They include direct citations, encouraging click-through to sources
- They’re dynamic, adjusting based on user interaction
What this means for content creators:
- Your content might get cited without ranking #1
- High-quality, well-structured content has more chances for visibility
- Citations in AI Overviews can drive significant traffic
- Being cited in AI Overviews often leads to improved traditional rankings
The story of how platforms work together becomes clearer when we look at specific examples. Take the case of technical documentation:
- User searches Google for error message
- Finds forum posts but no clear solution
- Asks Perplexity to explain the forum solutions in simpler terms
- Returns to Google for specific documentation
- Uses ChatGPT to generate step-by-step instructions based on all gathered information
The evolution of search behavior Traditional search engines still dominate because they excel at:
- Visual content (images, videos, product photos)
- Recent news and time-sensitive information
- Local business information
- Price comparisons and shopping
- Direct access to specific websites
The future is about understanding how traditional search engines and generative engines complement each other. Just as a well-rounded education includes both lectures and self-study, a well-rounded content strategy needs to embrace both platforms. The key is understanding how to make your content valuable and accessible regardless of how people discover it.
Practical optimization strategies for each platform type
When one of our clients approached us, they were excelling in traditional SEO but had zero visibility in AI-generated responses, particularly Google’s AI Overviews. In just three months, we helped them grow from 0 to over 3,000 keywords appearing in AI-generated results by using a Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) strategy that goes beyond keyword stuffing and link-building.
The way large language models (LLMs) source and generate information is fundamentally different from how search engines crawl and rank content. Winning in AI-generated responses requires different tactics: ones that optimize for context, citations, and structured data rather than just ranking factors.
Optimizing for static LLMs (ChatGPT Free, Claude, Gemini Basic)
Static pre-trained models like Claude, Gemini Basic, and free-tier ChatGPT operate using a fixed dataset with a knowledge cutoff. They do not pull in real-time search data, meaning that traditional ranking strategies won’t get you visibility here.
The strategy? Make your content “sticky” in model training data.
1. Get cited in widely recognized sources
LLMs rely heavily on established, authoritative sources when generating responses. If your content is referenced on Wikipedia, academic papers, industry reports, or government sites, it’s far more likely to be absorbed into future AI training data.
What we did for our client:
- Did digital PR outreach for research reports they had released to get cited in relevant publications
- Did surround sound SEO, making sure their brand name was also published in other high-ranking pages about the category they operate in, like “best [category] tools”
- Keep updating content to have the most up-to-date stats and expert resources
This significantly increased the chances of their insights being included in LLMs’ knowledge bases.
2. Structure content into definitive, quotable snippets
Unlike search engines, AI models don’t extract individual keywords. They synthesize entire concepts. Your content must be structured in a way that makes it easy for LLMs to “memorize” and cite.
✅ DO
- Use fact-based, definitive statements that are highly quotable
- Structure content in question-answer format (similar to FAQ schema)
- Keep sentences concise and self-contained
🚫 AVOID
- Writing in vague, opinion-heavy language
- Overloading articles with speculative or non-verified information
- Assuming AI models will “connect the dots”—they need explicit context
Example of a good snippet:
“The 2024 study by MIT found that AI-generated summaries reduce cognitive load by 40%, making them a preferred format for technical readers.”
LLMs can pull this exact phrasing into their responses.
Optimizing for search-augmented LLMs (ChatGPT Plus, Perplexity, AI Overviews)
Search-augmented models like ChatGPT Plus with browsing, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews behave more like hybrid search engines, pulling in real-time data to supplement their pre-trained knowledge.
Here’s how to ensure your content is actively cited rather than just passively stored.
3. Schema markup for AI citations
While traditional SEO relies on structured data for SERPs, AI-driven platforms use it to extract authoritative responses.
What we implemented for our client:
- Used schema.org Speakable markup to highlight AI-friendly quotes
- Implemented FAQPage schema to structure content in an answerable format
- Used Article schema with author credentials to reinforce E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
4. Optimize for real-time web crawling (Perplexity & ChatGPT Plus)
Perplexity and AI-enhanced ChatGPT browse the web in real-time, which means they are highly sensitive to content freshness and high-quality citations.
✅ DO
- Publish frequent updates to key pages to trigger recrawls
- Create data-driven studies that AI models will reference
- Monitor crawl logs to identify how often PerplexityBot visits your site
🚫 AVOID
- Relying on static evergreen content without updates
- Creating listicle-heavy content with no original research
- Ignoring real-time engagement signals like CTR and bounce rates
5. Write for NLP
AI-driven chatbots and content generation tools rely on natural language understanding (NLU) to process text and generate meaningful responses. However, most traditional writing styles don’t account for how AI parses information.
Natural language understanding (NLU) is a branch of AI that enables computers to comprehend human language beyond just recognizing words. Unlike basic text processing, which focuses on identifying keywords, NLU interprets context, meaning, sentiment, and intent. It allows AI systems, such as chatbots and virtual assistants, to generate relevant, human-like responses rather than relying on rigid scripts.
For example, if a customer asks, “Can I return this item?”, a basic chatbot might match the keyword “return” and provide a generic return policy. An NLU-powered chatbot, however, understands the intent behind the question and may ask for an order number or clarify return conditions based on context.
Optimizing content for AI involves structuring language in a way that makes parsing easier and allows the system to extract key information effectively. This is crucial not only for chatbot development but also for SEO, where AI-driven search engines increasingly prioritize content clarity and structure.
What is parsing, and why does it matter?
Parsing is the process by which AI breaks down text into structured components to extract meaning. It involves identifying parts of speech, analyzing sentence structure, and mapping words to concepts in a knowledge base.
For example, when an AI encounters the sentence:
“Customers expect fast responses from chatbots.”
It might parse it as:
- Subject: customers
- Verb: expect
- Object: fast responses
- Prepositional phrase: from chatbots
This breakdown helps AI understand the relationship between words and derive meaning from text. However, if a sentence is overly complex, ambiguous, or lacks context, AI might misinterpret it.
Poorly structured text:
“In a world where instant gratification is the norm, businesses must rise to the challenge by leveraging chatbot solutions that deliver swift responses to customer queries.”
AI-friendly version:
“Customers today expect instant responses. Businesses can use chatbots to meet this demand by providing fast answers to customer questions.”
The second version is clearer, easier to parse, and more useful for AI-driven applications.
How to write in a way that’s easier for AI to process
- Use clear, concise sentences
- Avoid unnecessary complexity. Shorter sentences with clear subjects and verbs are easier for AI to process.
- Instead of: “Chatbots, which have been increasingly used by enterprises across various industries, are designed to improve efficiency and customer experience.”
Try: “Enterprises use chatbots to improve efficiency and customer experience.”
- Limit ambiguity
- AI struggles with vague references and pronouns. Always provide clear subjects.
- Instead of: “This is why companies invest in automation.”
Try: “Companies invest in automation to improve efficiency and reduce costs.”
- Use structured formatting
- AI reads structured content more efficiently. Use:
- Bullet points for lists
- Subheadings to break up sections
- Numbered steps for processes
- AI reads structured content more efficiently. Use:
- Include context in keyphrases
- Instead of: “It improves operations.”
Try: “AI-powered chatbots improve customer service operations by reducing response time.”
- Instead of: “It improves operations.”
Applying this to SEO writing
SEO has traditionally focused on keyword optimization, but AI-driven search engines prioritize content that provides clear, structured answers. Writing in a way that makes parsing easier helps both chatbots and search engines extract meaning from text.
Before: traditional SEO writing
“Chatbots are AI-driven tools that help businesses engage with customers. Many companies use chatbots for customer support, and chatbot technology is improving with advancements in AI.”
After: SEO + NLP-optimized writing
“AI-powered chatbots help businesses engage with customers by providing instant responses. Companies use chatbots for customer support, reducing wait times and improving satisfaction. With advancements in AI, chatbots can now understand user intent and provide context-aware replies.”
The second version:
- Uses short, clear sentences
- Provides structured information
- Incorporates context into keyphrases
- Improves readability for AI and humans
Measuring generative engine optimization success
How do you know if all of this is working?
The keyword in itself is slowly dying as a planning use case. When a single page can rank for hundreds or even thousands of keywords, trying to track for a single keyword is starting to make less and less sense.
And this becomes even clearer when you consider how people use LLMs. You can type in the same question an infinite amount of ways – it wouldn’t make sense to track visibility for a single question or key phrase.
So we want to look at overall visibility. Right now, what we can track is referral traffic from LLMs and appearances in AI overviews.
The future of generative engine optimization
Generative engine optimization (GEO) is evolving rapidly as AI-driven search engines and large language models (LLMs) redefine how content is surfaced and consumed. Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on ranking for specific keywords, GEO prioritizes optimizing content for AI comprehension, retrieval, and citation in AI-generated search results.
As AI-generated overviews become more prevalent in search engines, businesses must adapt their content strategies to stay visible and relevant.
AI-driven search is shifting visibility metrics
Search engines now generate answers rather than just pages, at least, for many answers. Google’s AI overviews and tools like Perplexity AI are already changing how users interact with search results. Instead of clicking through to multiple sources, users increasingly rely on AI-generated summaries, which means ranking #1 isn’t as valuable as being referenced in AI-driven results.
What this means for GEO:
- Focus will shift from keyword rankings to AI citations and visibility in generative responses.
- Referral traffic from AI-generated summaries will become a key success metric.
- Structured, AI-readable content will outperform traditional keyword stuffing.
Structured data and entity optimization will matter more
AI models rely on structured data and knowledge graphs to generate accurate responses. Content that is well-organized, semantically rich, and explicitly linked to entities will be more likely to be featured in AI-generated answers.
What this means for GEO:
- Schema markup and structured metadata will become essential.
- Content must be contextually rich, connecting key entities in a way AI can process.
- Websites that provide clear, authoritative, and well-cited information will have a competitive edge.
Measuring success in a post-keyword world
As AI search engines move beyond keyword-based ranking, businesses will need new ways to measure content success. Traditional SEO metrics (e.g., page rankings, organic CTR) may become less relevant, replaced by AI-driven visibility metrics like:
- Appearance in AI-generated summaries (Google AI overviews, Perplexity citations).
- Referral traffic from AI-generated search answers.
- AI-assisted engagement (e.g., voice search interactions, chatbot citations).
The next steps for content creators
To stay ahead, businesses and content marketers should:
- Optimize for AI citation and retrieval, not just keyword rankings.
- Use structured data and clear entity relationships in content.
- Create scannable, modular, and AI-friendly content formats.
- Monitor AI-driven referral traffic and visibility as key performance indicators.
